By Wang Hongqiu, Wang Chunjiao, PetroChina Petrochemical Research Institute
PP self-sufficiency increases year by year
In 2019, China's Polypropylene capacity and output were 27.03 million t/a and 23.2 million tons, respectively. The market has seen competitions among state-owned enterprises like Sinopec, PetroChina and CNOOC, joint ventures such as Sinopec Sabic Tianjin PC, Sino-Korea (Wuhan) Petrochemical, and CNOOC Shell, private enterprises like Hengli Petrochemical and Zhejiang Petrochemical, coal chemical enterprises, propane dehydrogenation enterprises and imported products. Among them, Sinopec has the largest capacity, accounting for 26% of the total, followed by PetroChina, accounting for 18%. From the perspective of raw materials, oil-based PP accounts for 59% of the total, followed by coal-based PP and propane dehydrogenation routed PP, accounting for 25% and 9%, respectively.
With the release of new capacities, PP capacity is expected to exceed 35 million t/a by 2023, with a self-sufficiency rate of nearly 90%, as shown in Chart 1. Except for the high-end products, the supply and demand will be basically balanced by then, and market competition will be fiercer.
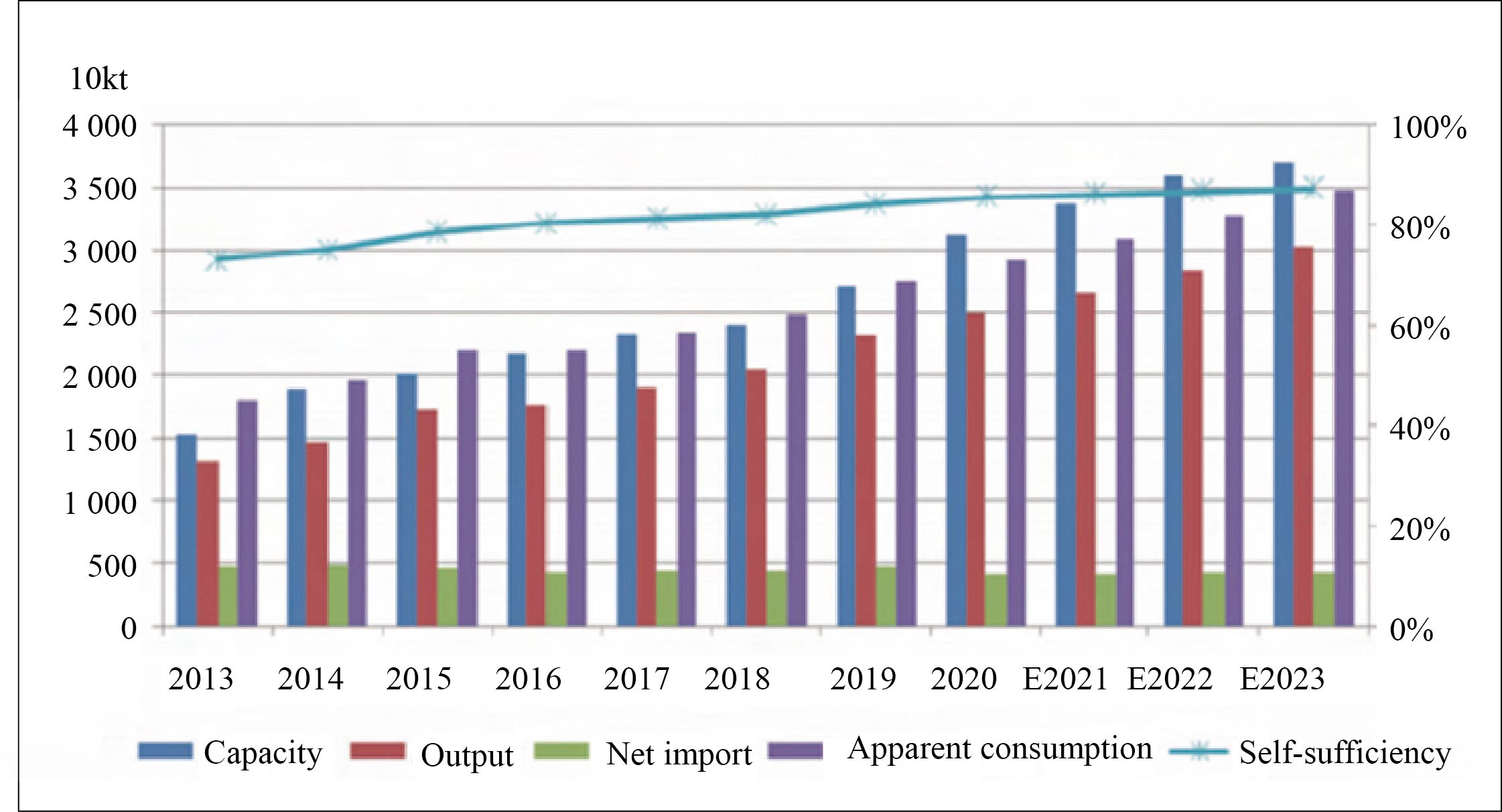
Chart 1 China’s PP supply and demand, 2013-2023
PP consumption takes 37% of global total
In 2019, China's PP consumption was 28.02 million tons, accounting for 37% of global PP consumption. In China, PP products are mainly used in the production of woven, film, and injection molding products, of which yarns and injections respectively account for 37% and 27%, films & sheets 24%, fibers 8%, and pipes 4%, as shown in Chart 2. The growth rate of PP demand in the future will gradually decline.
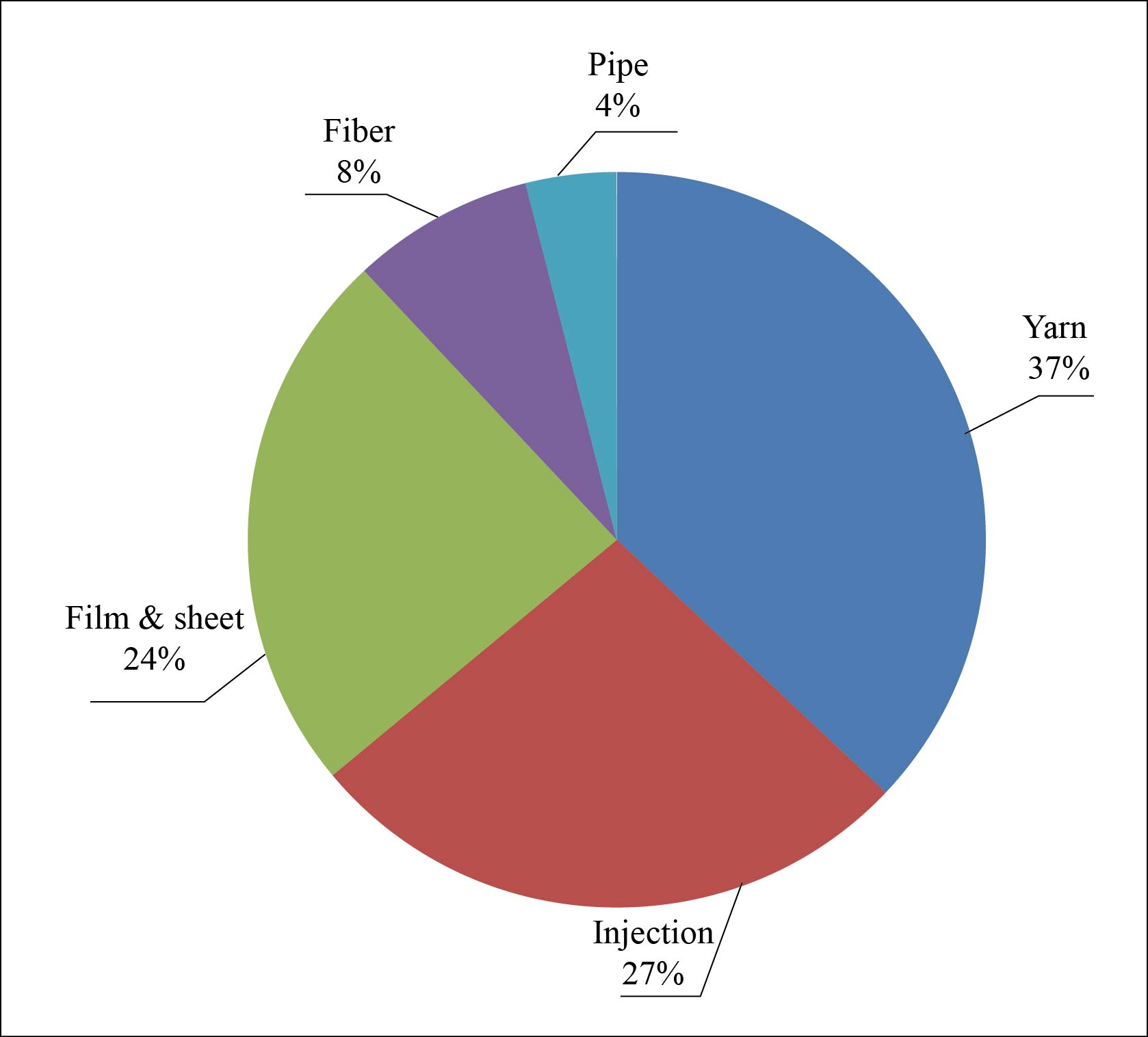
Chart 2 China’s PP consumption structure
PP yarn is mainly applied to woven products, like the outer packaging of cement, chemicals, grain, feed and construction materials, of which the consumption from cement bags is the largest. With the increasing stringency of environmental protection policies and regulations such as plastic restrictions, the demand for packaging of cement and building materials, disposable plastic straws and toothbrushes is decreasing. The share of PP yarns in the whole pie will continue to decrease.
PP injection is mainly used in small household appliances, daily necessities, washing machines, toys, automobiles, and totes. Despite the rapid increase in demand for all kinds of small home appliances, the growth rate of PP injection slowed down due to the decline in the growth of automobile sales and the tightening of real estate policies.
PP films are mainly used in the field of food packaging, and can be divided into BOPP film, CPP film and IPP film according to the processing technology. The demand for BOPP film is the largest, but it has been replacing by yarns recently, on the back of yarns’ low price. Meanwhile, CPP special film’s ratio is increasing, leaving the overall PP film’s percentage stable in the whole pie.
PP fibers are mainly used in the fields of decoration, clothing, medical and health. With the implementation of the second child policy and the aging of the population, especially the outbreak of the covid-19 pandemic, the market demand for downstream wet wipes, diapers, masks and other health protection has surged, resulting in a shortage of fiber materials in China.
PP pipes are mainly used in water supply and heating systems. It has the advantages of light weight, convenient in transportation, good environmental performance, and being recyclable. With the progress of urbanization and winter heating of the South, the demand for the pipes is on the rise.
High-end PP still needs to be imported
In 2019, China’s mainland imported 3.491 million tons of PP in primary forms (homopolymerized PP), 1.55 million tons of ethylene-propylene polymer (copolymerized PP), and 182 000 tons of other propylene copolymers in primary forms, with a total import volume of 5.223 million tons, mainly from South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, Japan, and Middle East.
In recent years, with the release of new capacities in China, exports have shown a rapid upward trend, reaching 406 000 tons in 2019, a year-on-year increase of 13.8%. The products are mainly exported to neighboring regions such as Vietnam.
From the perspective of import categories, homo polypropylene still accounts for the largest proportion, and the overall trend is a gradual decline. The proportion of copolymerized PP is relatively small, but it is on the rise, and the average price is also higher than the average price of homopolymerized PP and the overall average price of PP imports. See Chart 3 for details.
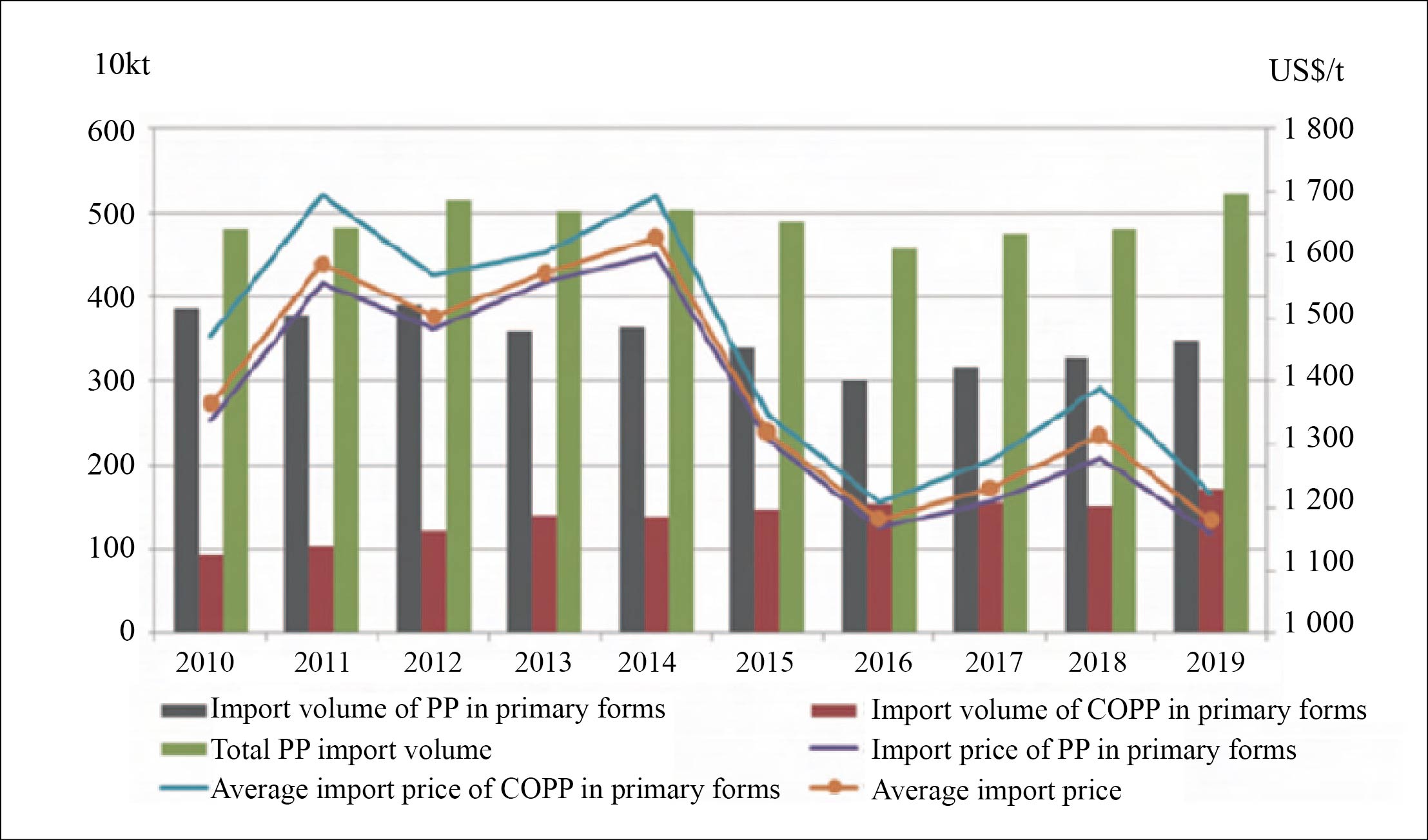
Chart 3 China’s PP import volume and import price, 2010-2019
Some high-performance and special products, such as metallocene PP, special BOPP film, CPP film, etc. still need to be imported in large quantities to meet the domestic market demand. The annual consumption of metallocene PP in China is about 100 000 tons, while the domestic supply is very tight with only one supplier, Yanshan Petrochemical. It is mainly used for the production of high-transparent PP products for medical use, food packaging films, non-woven fabrics, ultra-fine polypropylene fibers, etc. Annual imports of PP film materials such as special BOPP films, electrical films, capacitor films and aluminized films, with high stretching speed and width, ultra-thin, ultra-transparent and better low-temperature heat sealing performance, and PP injection plastics for automobiles and home appliances are all over one million tons. The annual import volume of PP pipes is about 500 000 tons.
PP imports enter China mainly through the southeastern coastal area, accounting for 90% of the country's total imports. Among them, Guangdong has been ranking No. 1 for many years, taking 34.4%; Zhejiang Province ranks second, taking 23.7%. This is mainly because most of the PP processing enterprises and downstream users are concentrated in the southeast coastal area. The demand for PP in East China accounted for about 35.6% of China's total demand, following by South China, accounting for about 30%.
Decline in demand and cost drags down PP prices
Decline in demand and cost lowers PP prices. Since the naphtha cracking is still the main source of PP raw materials in the world and China, the prices of PP products and those of naphtha and crude oil are closely related, as shown in Chart 4.

Chart 4 Market prices of PP, propylene, naphtha, and crude oil
Overall, China's PP prices were under pressure in 2019. On the supply side, the anticipation of launching of domestic and world large-scale new capacities resulted in continuous pressure increase; on the demand side, affected by the slowdown in economic growth, the downstream growth rate was weaker than expected, and the prices of PP products continued to fall.
Since the beginning of 2020, due to the covid-19 pandemic, the downstream demand has further weakened. The feedstock has been affected by the rapid decline in crude oil prices. PP prices will continue to fluctuate at a low level.
In recent years, China's PP industry has experienced capacity expansion and new product development. The overall level has been significantly improved, and the product self-sufficiency rate has reached 83%. In the future, as new projects are put into production, the raw materials and market players will become more diversified, and market competition will become more intense.