By Zhang Guihua, Lu Hui, Research Institute of CNPC Jilin Petrochemical
Capacity to increase rapidly
There are 13 cumene-based phenol/acetone companies in China, with capacities totalling 2.548 million t/a (excluding Gaoqiao Petrochemical’s idled 100 kt/a phenol and 60 kt/a acetone plant in its old production site). Details are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 China’s phenol/acetone capacities in 2018
Region | Producer | Phenol capacity (kt/a) | Remarks |
East China | FCFC Ningbo | 300 | Started up in Jan 2015 |
Changchun Chemical (Jiangsu) | 300 | Started up in Aug 2013 | |
CEPSA Chemical (Shanghai) | 250 | Started up in Jan 2015 | |
Sinopec Mitsui Chemicals | 250 | Started up in Dec 2014 | |
Shandong Lihuayi Weiyuan | 220 | Started up in Oct 2012 | |
Shiyou Chemical (Yangzhou) | 200 | Started up in May 2012 | |
Sinopec Gaoqiao | 150 | ||
South China | CNOOC Huizhou Refining & Chemical | 220 | Started up in Dec 2017 |
Huizhou Zhongxin Chemical | 120 | Started up in Jan 2008 | |
North China | Sinopec SABIC Tianjin | 220 | Started up in 2009 |
Sinopec Yanshan | 160 | ||
Northeast China | PetroChina Jilin | 83 | Capacity expanded in 2013 |
BlueStar New Materials (Harbin) | 75 | Capacity expanded in 2015 | |
Total | 2 548 |
China’s phenol capacity will continue to increase in the next few years. New capacities are designed to be built with downstream bisphenol A (BPA) plants. FCFC Ningbo and Zhejiang Petrochemical are moving faster in their new plants’ start-up. Capacity additions amount to 1.55 million t/a, which will boost the total domestic phenol capacities to 4.098 million t/a.
Table 2 New phenol plants in China
Producer | Phenol capacity (kt/a) | Start-up time (E) |
FCFC Ningbo | Capacity expanded from 300 to 400 | 2020 |
Zhejiang Petrochemical (Zhoushan) | 400 | 2020 |
Jingang Petrochemical (Jinzhou, Liaoning) | 220 | 2020 |
Liaocheng Luxi Polycarbonate (Liaocheng, Shandong) | 210 | |
ChemChina Tianjin Petrochemical | 220 | |
Wanhua Chemical | 400 | |
Total | 1 450 |
Consumption structure undergoes fundamental changes
China’s phenol output reached 1.878 million tons in 2018, up by around 0.6% year on year. Its import volume stood at 419 kt and export volume at 44 kt. Apparent consumption in China totalled 2.253 million tons, up by 3.6% year on year. Table 3 shows the domestic phenol supply-demand balance in recent five years. Figure 1 shows domestic phenol consumption structure in 2018.
Table 3 China’s phenol supply-demand balance in 2013-2018 (kt)
Year | Output | Import volume | Export volume | Apparent consumption volume |
2013 | 1 130 | 365 | 6 | 1 530 |
2014 | 1 362 | 217 | 39 | 1 540 |
2015 | 1 618 | 173 | 18 | 1 740 |
2016 | 1 640 | 248 | 57 | 1 888 |
2017 | 1 866 | 366 | 57 | 2 175 |
2018 | 1 878 | 419 | 44 | 2 253 |
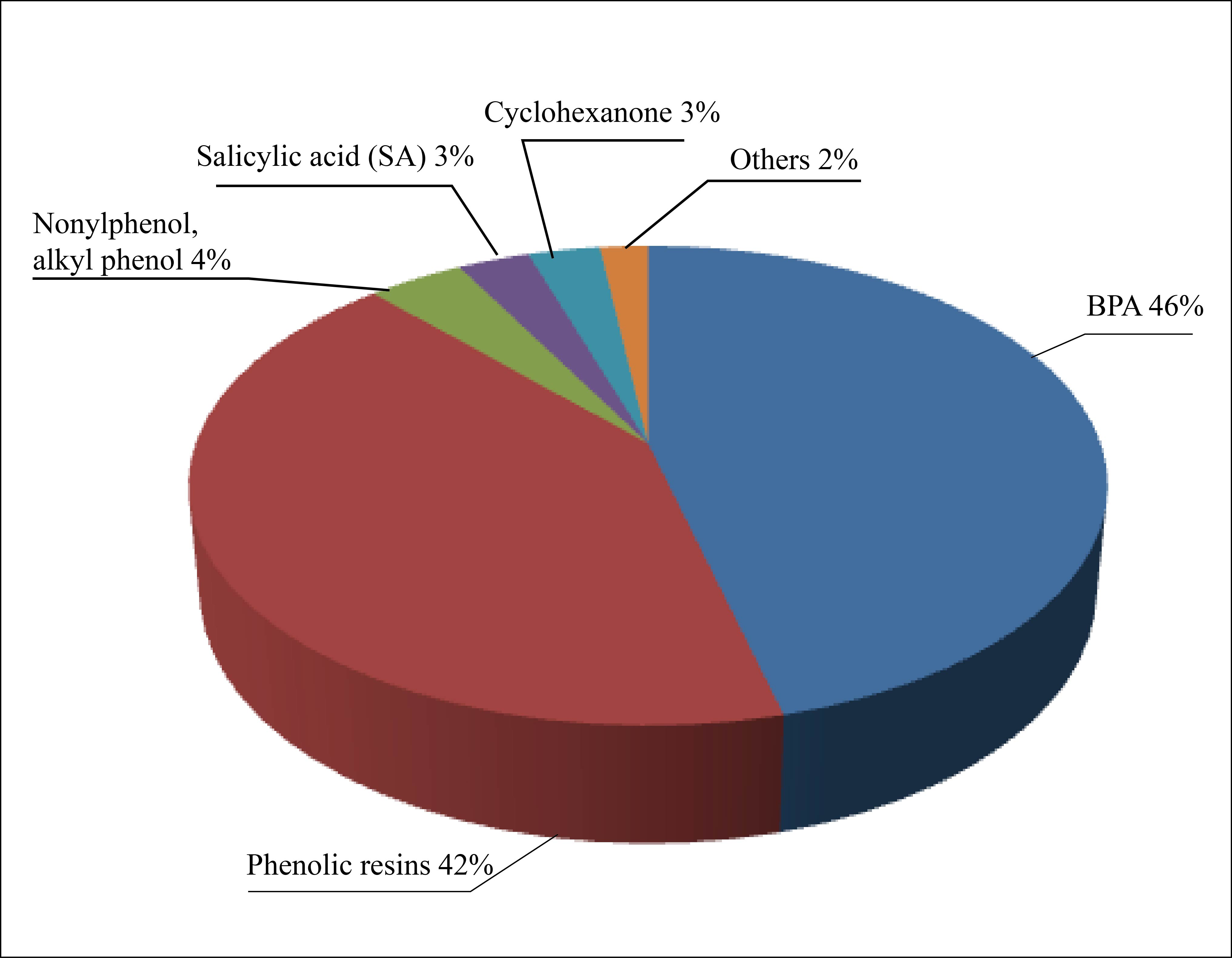
Figure 1 Domestic phenol consumption structure in 2018
Domestic phenol consumption exceeded 2.20 million tons in 2018. The concentrated start-up of a large number of new BPA plants has brought about fundamental changes in China’s phenol consumption structure. BPA has overtook phenolic resins to become the largest phenol consumer, accounting for 46% of the total domestic consumption, followed by phenolic resins, at 42%. Phenol consumption from the cyclohexanone industry has been rising, after Fujian Shenyuan New Materials’ new plant launched production in July 2017. Moreover, if Jiangsu Weiming Petrochemical’s two 150 kt/a phenol-based cyclohexanone plants start up as scheduled, cyclohexanone’s influence on phenol consumption will increase significantly, with its share likely to top 10%.
Demand from other downstream phenolic resins, nonylphenol and SA industries will unlikely pick up, as hampered by environmental protection constraints or bearish end-user demand. Their phenol consumption is poised to drop.
Downstream demand structure of China’s phenol industry is expected to change constantly in the coming years. BPA will remain the largest phenol consumer, while phenolic resins will take a smaller share with its demand shrinking, and cyclohexanone is likely to emerge as a major driving force of phenol demand.
Phenol imports from South Korea take up 40%
China imported 419 kt of phenol in 2018, up by 14.5% year on year. South Korea was the largest phenol import supplier to China, accounting for 41.1% of the total, followed by the US and Saudi Arabia, occupying 17.7% and 17.2% respectively. Table 4 shows China’s phenol import origins in 2018.
Table 4 China’s phenol import origins in 2018
Countries or regions | Import volume (kt) | Share (%) |
South Korea | 172 | 41.1 |
The US | 74 | 17.7 |
Saudi Arabia | 72 | 17.2 |
Thailand | 60 | 14.2 |
Others | 41 | 9.8 |
Total | 419 | 100 |
China’s phenol import volume is expected to decrease, as the start-up of new domestic plants will ease the pressure from increasing demand.
China exported 44 kt of phenol in 2018, down slightly from 2017. Major export destinations include Taiwan and India, accounting for 34.1% and 25.0% respectively of the total.
Future development
Cumene-based phenol/acetone production is the mainstream process but easily causes excess acetone supply. Therefore, many countries are striving to develop other phenol production processes, such as direct oxidation of benzene to produce phenol, which has become the hotspot of research and development. Oxidants used for direct oxidation include oxygen, hydrogen dioxide (H2O2), nitrogen oxide (N2O) etc. Research results showed that the benzene conversion rate is lower when molecular oxygen is used as oxidant than N2O or H2O2 is used as oxidant. These two oxidants apply easier process, which is less harmful to environment and has high yield ratio, thus demonstrating the potential for industrial development and application.
Enterprises are mulling over large-scale production of phenol/acetone to bring down their production costs, enhance product quality and strengthen their competitiveness. They shall adopt integrated production mode, such as building supporting downstream BPA, polycarbonate and epoxy resins plants of vast growth potential and high added-value to form a complete industrial chain, leading by phenol, so as to avoid market risks.