By Sang Jianxin, China National Chemical Information Center
Imports continue to increase due to short domestic supply
In 2018, on the back of the recovery of end demand and the industry boom, the market prices of polyester products hit a new high in recent years. China's polyester capacity and production increased steadily. PET exports also increased significantly compared with previous years, and the sharply rising operating rates have driven the demand for MEG. China's ethylene glycol demand in 2018 is expected to reach 16.45 million tons, an increase of 14% YoY.
China's ethylene glycol capacity and output have grown rapidly, but the supply is still not able to meet the ever-growing market demand. The long-term self-sufficiency rate of ethylene glycol is only 40%, and the import volume is expanding year by year. In 2018, China's ethylene glycol imports reached a record high. From January to November, the import volume reached 9.061 million tons, an increase of 13.5% over the same period of 2017, which was 7.98 million tons.
Coal-to-MEG rises to the occasion and commissioning peak appeared since 2017
At present, China's ethylene glycol products are produced via ethylene oxidation method (petroleum synthesis route), coal-based synthesis gas method or MTO method (methanol to olefin and ethylene to MEG). By the end of 2018, petroleum routed products are the main source of supply in China. The gap between supply and demand has triggered the development of coal-based ethylene glycol. The low investment and the short construction period have become the main edges of coal-based MEG, and the production capacity is increasing.
In 2018, coal-based ethylene glycol projects were intensively put into operation. The newly added ethylene glycol capacity during the year was 2.14 million t/a, of which the newly added coal-routed capacity was 1.74 million t/a. By the end of 2018, China's ethylene glycol capacity has reached 10.51 million t/a, including 4.42 million t/a coal-to-MEG, which has exceeded 42% of the total capacity.
At present, there are 20 new or proposed ethylene glycol projects, with a total capacity of 7.26 million t/a.
It is estimated that 18 ethylene glycol projects will be completed in China in 2019, with an additional capacity of 6.46 million t/a, and the total capacity of ethylene glycol is expected to reach 16.97 million t/a. Among them, the newly added coal-to-MEG capacity will be 5.36 million t/a, and the total coal-to-MEG capacity will be 9.78 million t/a by then, accounting for 58% of the total MEG capacity. The coal-based ethylene glycol capacity will become the dominant factor. There are two ethylene glycol projects planned to be put into operation in 2020, and the newly added capacity will be 0.8 million t/a. These two new projects will adopt the coal-to-syngas method. By the end of 2020, China's coal-to-MEG capacity will reach 10.58 million t/a. It accounts for 60% of the total ethylene glycol capacity. The new ethylene glycol capacity in China from 2017 to 2020 is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 New MEG capacity in China, 2017-2020 (kt/a)
Year | New capacity | Coal-to-MEG capacity | Total capacity | Proportion of Coal-to-MEG (%) |
2017 | 800 (coal-to-MEG 76, MTO route 4) | 2 720 | 8 370 | 32.5 |
2018 | 2 140 (ethylene routed 400, coal-to-MEG 1 740) | 4 460 | 10 510 | 42.4 |
2019 | 6460 (coal-to-MEG 5 360, integrated ethylene routed 800, MTO 300) | 9 820 | 16 970 | 57.9 |
2020 | 800 (coal-to-MEG 800) | 10 620 | 17 770 | 59.8 |
Operation becomes stable but product quality needs to be improved
Most of the coal-based ethylene glycol units put into operation in 2018 have achieved stable operation, with an average utilization of 71%, close to the ethylene-routed lines’ 76%.
However, compared with ethylene-routed products, coal-based ethylene glycol has the following three problems: 1) Product stability is poor, and different batches of products from the same line can either meet the standard or not; 2) As for the production of polyester bottle chips, the coal-based ethylene glycols have poor transmittance; 3) Coal-based ethylene glycol has effect on the dyeing of some polyester filament products and is not suitable for the production of fine denier. Therefore, so far, no polyester producers use only coal-based ethylene glycol as raw material. In addition, most of the exported polyester fiber products do not use coal-based ethylene glycol as feedstock. The main reason is that the major export destinations such as the EU have higher raw material requirements. Meanwhile, as polyester bottle chips are mostly applied in food sector such as drinking bottles, where the food safety requirements are higher, no producers accept coal-to-MEG now.
MEG futures’ impact on coal-based products
On December 10, 2018, ethylene glycol futures were listed on the Dalian Commodity Exchange (hereinafter referred to as DCE) and became the world's first ethylene glycol futures product.
Since coal-based ethylene glycol cannot meet the stability requirements in terms of quality and output, it has not been included in the transaction. In the "Glycol Futures Contract Design Specification" issued by DCE, the ethylene glycol contract is marked as ethylene glycol produced via ethylene route, with impurities index such as 1,2-butanediol and ethylene carbonate so as to distinguish ethylene routed products and coal-to-MEG.
Although not involved in the transaction, coal-based ethylene glycol producers still need to pay attention to the development of ethylene glycol futures, especially focusing on price movements. Due to the long industrial chain of ethylene glycol, international crude oil prices, commodity cycles, raw material supply, downstream demand and other factors may all have impacts on product prices. For a long time, the price fluctuation of China's ethylene glycol spot market has not only plagued polyester enterprises, but also affected the production and operation of ethylene glycol enterprises. The lowest and highest price curves of China's ethylene glycol through 2012 to 2018 are shown in Chart 1.
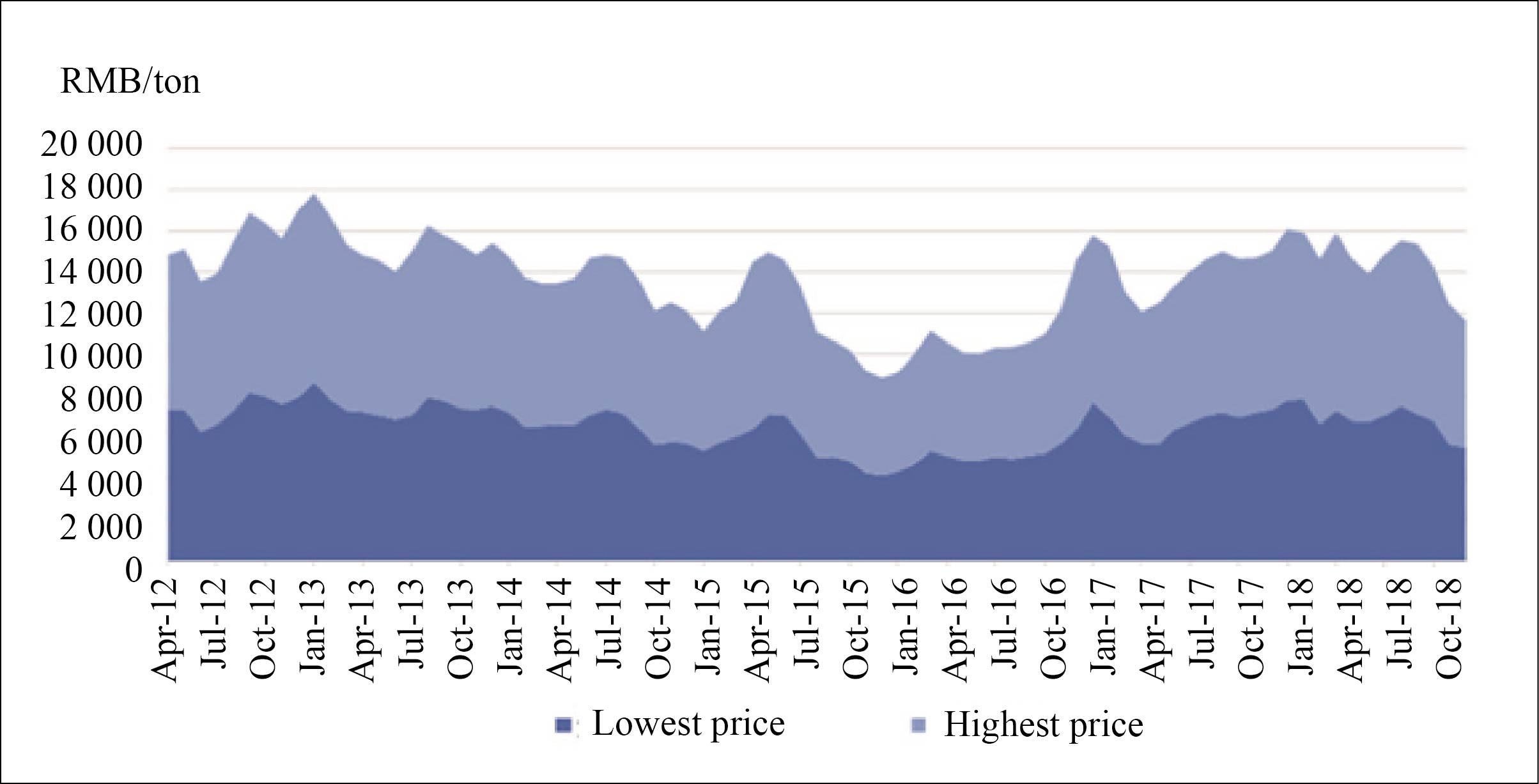
Chart 1 Lowest and highest MEG prices in China, 2012-2018
The domestic ethylene glycol contract pricing system is dominated by Sinopec. However, due to the high import dependency, the ex-works prices of Sinopec and PetroChina are also passively influenced by importers’ prices. With the listing of futures, the price of ethylene glycol products is expected to stabilize.
Quality improvement, energy consumption reduction and clean production are the top priorities
Coal-to-MEG contributes the main new capacities in the next two years, and it is likely to enter the commissioning peak in the second half of 2019. More than 90% of China's ethylene glycols are applied to polyester production. Although coal-based ethylene glycols are gradually accepted by polyester producers, the use of coal-based goods is still limited due to differences in quality between coal-to-MEG and ethylene routed MEG. If coal-to-MEG producers do not improve the quality and thus increase the acceptance of polyester companies, structural overcapacity might occur. The price of coal-based ethylene glycol is lower than that of ethylene-process products, which can reduce the cost of downstream enterprises. Therefore, upgrading the quality and reducing consumption are the primary tasks of coal-to-MEG enterprises.
In addition, environmental protection requirements are becoming more and more strict, and coal chemical industry is the focus of environmental protection supervision. Such heavy pressure has forced many coal-based ethylene glycol manufacturers to shut down their plants. Therefore, coal-based ethylene glycol production technology still needs further innovation to minimize pollutant emissions and achieve energy conservation and emission reduction.